In the era where high-speed communication technologies such as Bluetooth and Wi Fi 6 are sweeping through, a modulation technology born in the mid-20th century - ASK/OOK - still plays an indispensable role in our lives: from the induction unlocking of car door keys to the status transmission of smart home sensors, its presence can be seen.
This communication method, which adopts the simplest "switch based" principle, occupies a core position in the field of short-range wireless control with almost zero power consumption and ultimate efficiency.
First, let's understand what ASK/OOK is?
ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying) is a common modulation technique that represents binary numbers 0 and 1 by changing the amplitude of the carrier signal; OOK (On Off Keying) is a special simplified form of ASK, which directly corresponds to the two-level system state through the "presence" and "absence" of the carrier wave. Both of these technologies have been around for a long time, but due to their simple implementation, stable system, and low cost, they have always been the mainstream solution for remote control devices (keyless entry systems, smart home systems, security systems, etc.).
Here are a few common ASK/OOK transmitter chips:
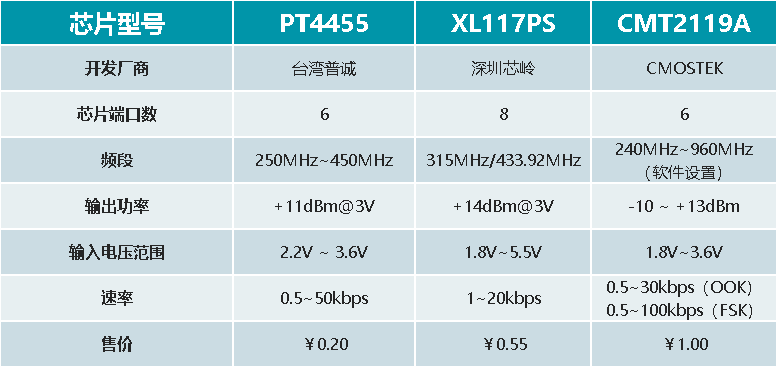
The data in the table is based on the chip manual provided
From the data in the table alone, we can see that PT4455 has an absolute price advantage over other related products in the frequency range of 250MHz~450MHz, and also has a significant advantage in data transmission rate.
Let's take a closer look at the internal components of PT4455, a highly cost-effective chip.
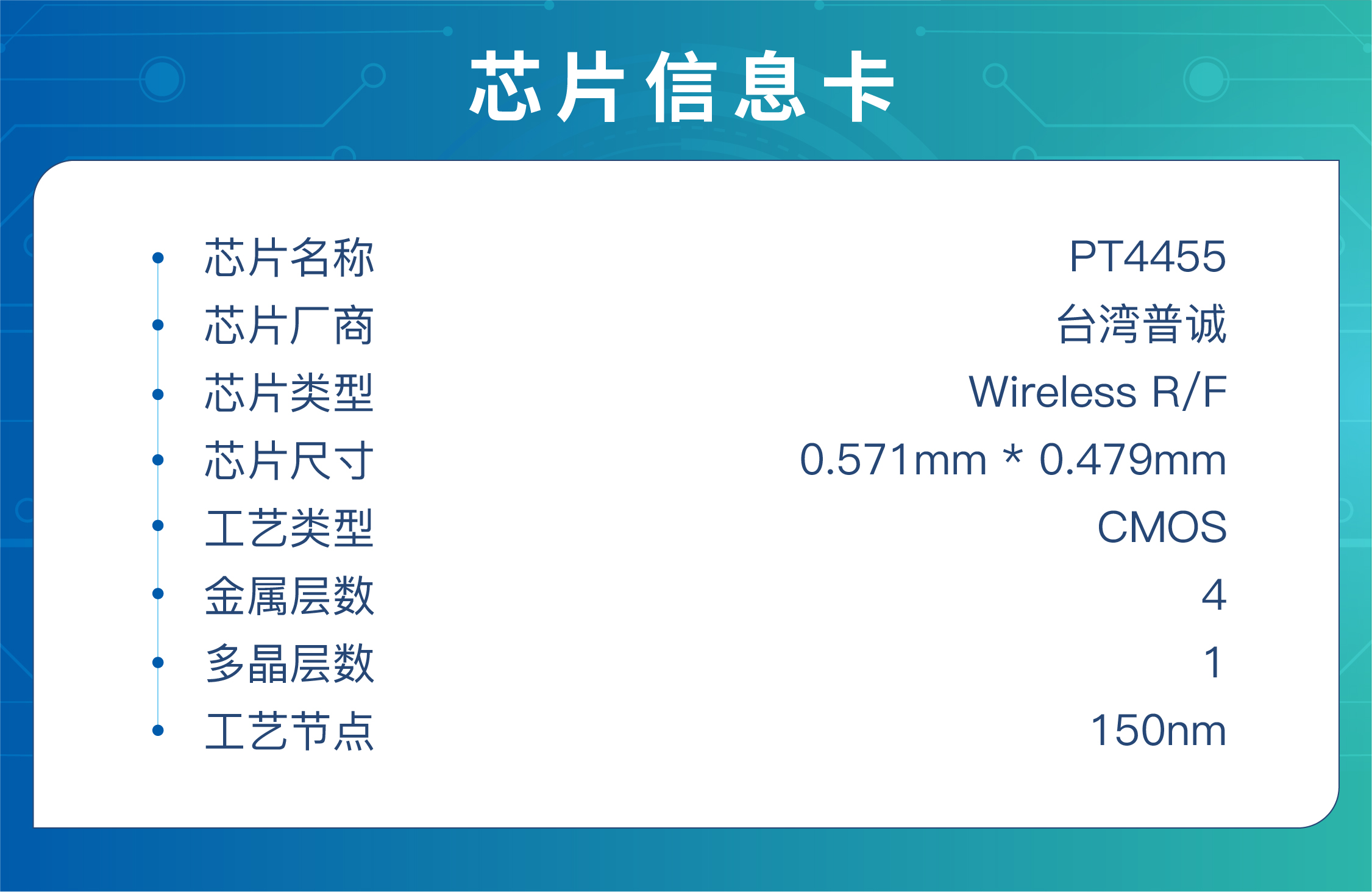
The data is provided based on the chip manual
PT4455 is a high-performance ASK/OOK transmitter with a simple structure. As shown in the top-level principle diagram below, the main structure of the chip is a phase-locked loop system, a monostable circuit, and a power amplifier. The phase-locked loop and power amplifier are controlled by the monostable circuit to enable rapid start-up when needed. When there is no signal from DIN, the circuit will automatically enter standby mode and enter a power-saving state of less than 1uA.
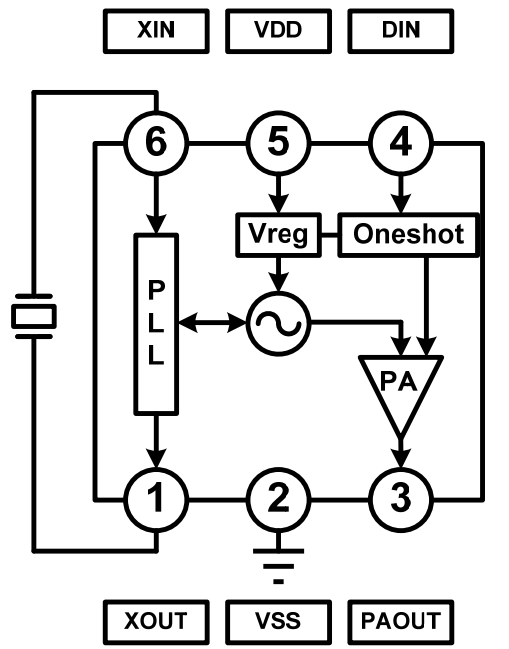
PT4455 Top Level Principle Block Diagram (Source Chip Manual)
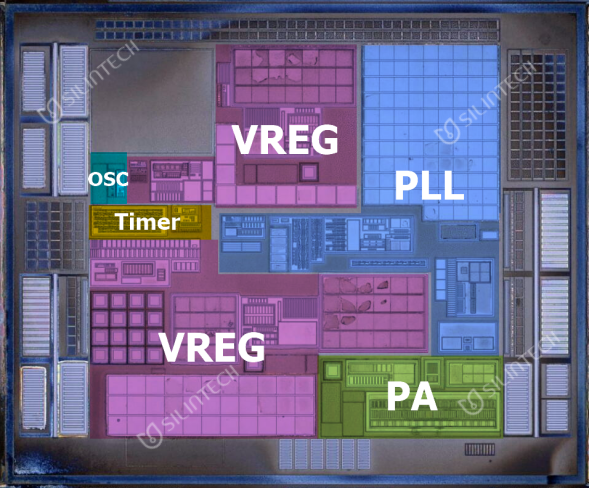
PT4455 Top Floor Floorplan
As shown in the following structural diagram, the reference clock of the chip comes from an external crystal oscillator, and the frequency range of 315MHz~433.92MHz is achieved through a 32 frequency divider in the phase-locked loop (see the frequency variation table in the figure below).
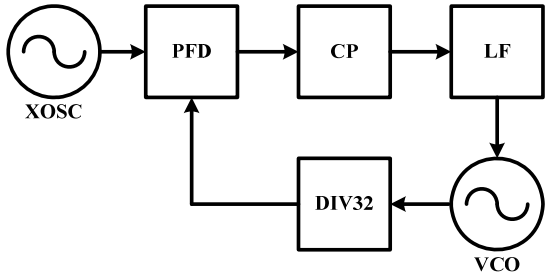
Phase Locked Loop (PLL) Structure Diagram (Source Chip Manual)
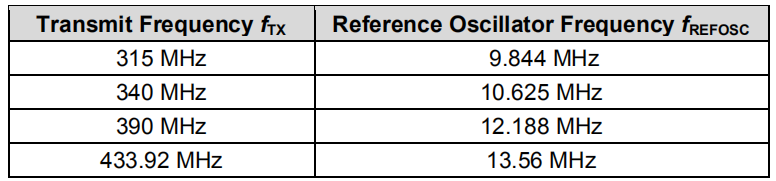
Frequency Variation Table (Source Chip Manual)
However, the start-up time of the crystal oscillator during signal transmission limits its wake-up time. Therefore, a monostable circuit is introduced to solve this problem. When the "High" signal is transmitted to DIN, the phase-locked loop and power amplifier will be turned on at the same time. When the "Low" signal is transmitted to DIN, the power amplifier will immediately turn off, and the phase-locked loop will be turned off after about 50ms under the delay control of the monostable circuit.
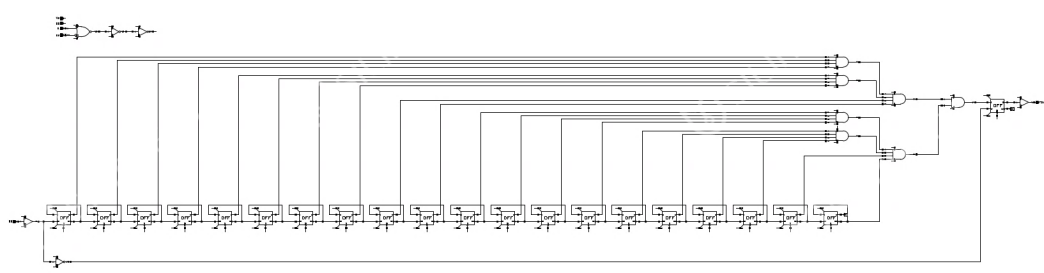
Schematic diagram of monostable circuit
Additionally, it is worth mentioning that the chip is designed with two sets of internal power supplies, one of which is dedicated to supplying power to the phase-locked loop to solve the interference problem of power amplifiers and crystal oscillators. This can also be seen from the floorplan in the above figure, which shows the schematic diagram of the voltage regulator. The two sets of voltage regulators inside the chip have the same structure.
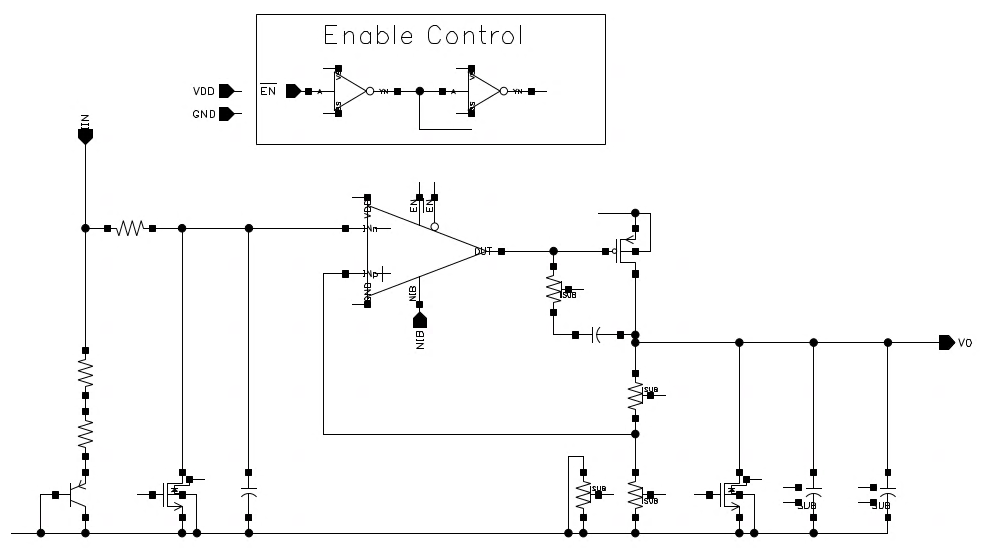
Schematic diagram of voltage regulator (source chip manual)
In today's explosive growth of IoT devices, PT4455 perfectly embodies the essential advantage of ASK/OOK technology - solving the most basic wireless control needs with the lowest cost, thanks to its core design of "minimalist circuit+μ A power consumption" (requiring only 6 peripheral components). With the popularization of smart homes, electronic price tags, and other scenarios, this "primitive yet reliable" technology will not only become a classic solution for remote controls, wireless sensors, and other scenarios, but also continue to play a "lightweight cornerstone" role in the wave of Internet of Things.

The above is today's sharing. If you need to learn more detailed technical information or have consultation needs related to cooperation, please feel free to contact us at any time. We will wholeheartedly provide you with professional answers and Technical Support.

